
If the company has too much debt, creditors may fear liquidity issues in case the company’s cash flows fluctuate or something happens to the company. It also shows a huge portion of debts in the total assets may minimize the creditor’s interest and increase the finance costs. Total assets include long-term assets & short-term assets include goodwill etc as per the balance sheet. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Therefore, maintaining a balanced proprietary ratio is crucial for any business.
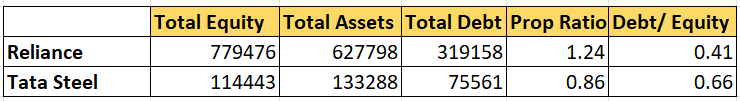
Example how to calculate Proprietary Ratio
The intent is to ascertain the risk involved and capital stability and also the cost of capital involved. The proprietary ratio is the proportion of shareholders’ equity to total assets, and as such provides a rough estimate of the amount of capitalization currently used to support a business. It empowers shareholders, creditors, and potential investors to assess the financial capability of a company to meet its long-term liabilities, revealing how much of the total funds are internal. The solvency ratio is a critical financial measure that evaluates a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations. It indicates the proportion of a company’s total assets financed by equity and debt, offering insight into the financial health and stability of a business. A higher solvency ratio suggests that the company is more capable of sustaining its debt load over time, while a lower ratio raises concerns about potential financial distress.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
- Proprietary ratio is very useful to the lenders, as it helps them ensure the safety of their investments by way of informing the level of dependence a corporation has on the outsiders’ funds.
- It is used as a screening device for financial analysis, a higher ratio, say more than 75% means sufficient comfort for creditors since it points towards lesser dependence on external sources.
- This means that 33% of the company’s total assets have been funded by the company proprietors.
- It indicates the proportion of a company’s total net worth (equity) relative to its total assets.
- It is calculated by dividing total assets (i.e., current assets and long-term assets) by tangible network.
How to Calculate the Proprietary Ratio
A high proprietary ratio—typically above 50%—indicates that the company relies significantly on equity financing rather than debt. This strengthens its balance sheet and makes it less vulnerable to interest rate changes or economic downturns. Companies with a high proprietary ratio are often perceived as more financially secure, which can positively influence their credit ratings and ability to secure financing at favorable terms.
The proprietary ratio is one type of solvency ratio that is not used like commonly used ratios and very few investors use the proprietary ratio. Proprietary ratio is very useful to the lenders, as it helps them ensure the safety of their investments by way of informing the level of dependence a corporation has on the outsiders’ funds. In simple words, a higher proprietary ratio is favourable since it depicts lower dependence on outsiders for funds, and hence, raises the firm’s credibility and creditors’ confidence.
The working capital turnover ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of sales by the net working capital. The liquidity ratio is used to measure a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations. Balance sheet ratios are calculations that use elements of a company’s balance sheet to measure its financial performance and health. A higher Proprietary Ratio, close to 1 or 100%, is generally considered good as it signifies that a larger proportion of the company’s assets are backed by the shareholder’s equity. However, a suitable ratio can vary depending on the industry and individual company circumstances. The proprietary ratio will also give shareholders an indication of how much they stand to receive in the event of the company’s liquidation.
Proprietary ratio is the one that is used to express a relationship between the amount invested by proprietors in the business and the total assets owned by the business. The proprietary ratio shows the latitude in which equity shareholders’ funds are invested in various types of company assets. This calculation will help you see the proportion of the company’s total assets that are funded by the proprietors versus other forms of financing.
The net profit (after tax) of a corporation is $150,000 and its fixed interest on long-term borrowing is $20,000. The term liquidity refers to the ability of a company the difference between fixed and variable costs to pay its short-term liabilities as and when they are due for payment. Or 75% meaning hereby that 25% of the funds have been supplied by the outside creditors.
Proprietors’ funds are also known as Owners’ funds, Shareholders’ funds, Net Worth, etc. This means that the company has financed 80% of its assets using its funds, which indicates that it is less reliant on external financing and has a strong financial position. We can use balance sheet ratios to help us understand how well a company is performing financially, how much debt it has, and how easily it could pay its debts if they came due.
It is used to assess financial stability, with a higher ratio indicating a stronger financial position. A high proprietary ratio signifies that a company is primarily financed by shareholders’ equity, reflecting strong solvency and financial health. On the other hand, a low proprietary ratio indicates higher reliance on debt financing, which increases the company’s financial risk and potential for instability. The proprietary ratio measures the amount of equity shareholders contribute toward the total assets of the business. The proprietary ratio (also known as net worth ratio or equity ratio) is used to evaluate the soundness of the capital structure of a company.

