The number of shares outstanding increases whenever a company undertakes a stock split. Stock splits are usually undertaken to bring the share price of a company within the buying range of retail investors; the increase in the number of outstanding shares also improves liquidity. As noted above, outstanding shares are used to determine very important financial metrics for public companies.
What is your current financial priority?
Similarly, if it uses the financial statements of one or more proir periods for comparison purpose, the shares for those periods must also be restated in the same way. It also includes shares held by the general public and restricted shares that are owned by company officers and insiders. The number of outstanding shares changes if the company issues new shares, repurchases existing is accounts receivable considered an asset shares, or if employee options are converted into shares. The term outstanding shares refers to a company’s stock currently held by all its shareholders. Outstanding shares include share blocks held by institutional investors and restricted shares owned by the company’s officers and insiders. A company’s number of outstanding shares is not static and may fluctuate wildly over time.
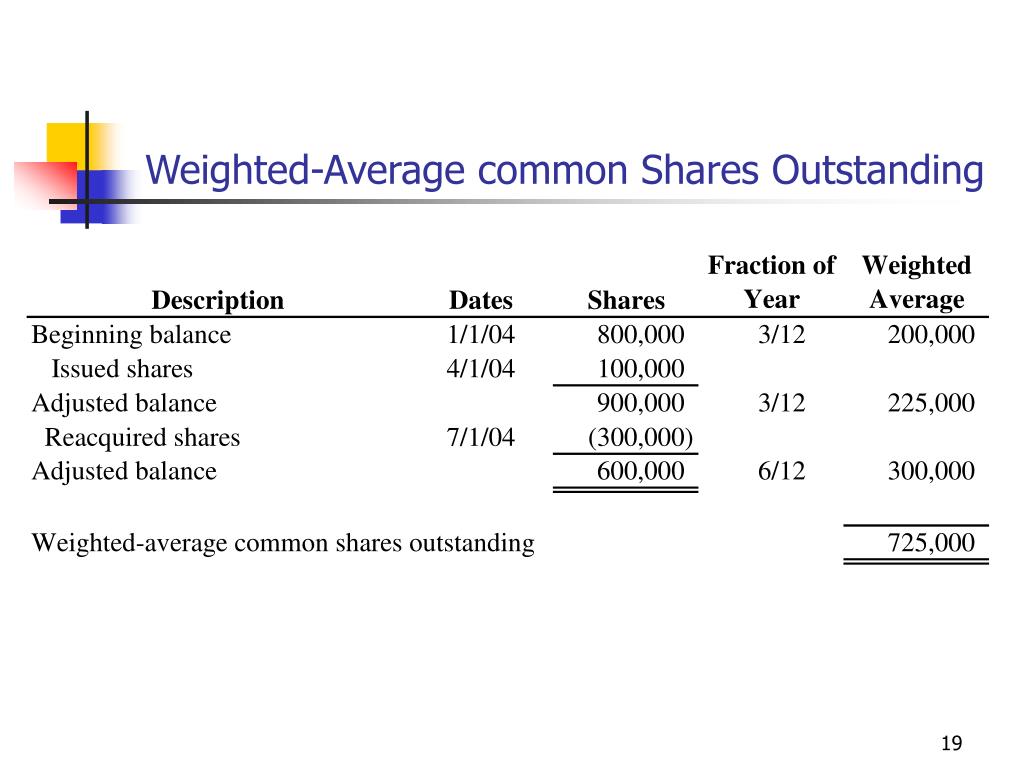
Calculating Weighted Average of Outstanding Shares
Because investors frequently purchase shares of a company at various times and in various amounts as they build their position in a stock, it can be a challenge to keep track of the cost basis of those shares. One method is for the investor to calculate a weighted average of the share price paid for the shares. The investor would multiply the number of shares acquired at each price by that price and then add those values together. Lastly, divide the total value by the total number of shares purchased to arrive at the weighted average share price.
How to Calculate a Company’s Weighted Average Number of Outstanding Shares
In case there is a large difference between basic and diluted EPS, investors should be aware of the possible increase in the number of shares outstanding in the future. In this example, the weights are calculated as 0.75 and 0.25, respectively, and the weighted average number of shares outstanding is 131,250. In the next row, input the number of months for which these values held true. The initial number of shares was maintained from January to September, or nine months, meaning there were only 75,000 shares outstanding for the remaining three months of the year. A weighted average is simply a method of determining the mean of a set of data in which certain points occur multiple times or in which certain points are valued more highly than others. Though the method of determining weights may vary, weighted averages are used in the calculation of a variety of technical indicators and financial metrics.
The weighted average is used by accountants reporting a company’s financial results in accordance with GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principals). CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path. Those with complex structures (those that have potential dilutive securities) must report both basic EPS and diluted EPS. Conversely, a decreasing WASO through share buybacks can be a positive signal, often leading to an increase in EPS and potentially boosting the stock price.
- When a company issues a stock dividend or exercises a stock split, it needs to restate its outstanding shares of common stock before the date of stock dividend or split to compute its weighted average number of shares.
- The weighted average of outstanding shares is a calculation that incorporates any changes in the number of a company’s outstanding shares over a reporting period.
- By contrast, a reverse stock split occurs when a company seeks to elevate its share price.
- The number of shares outstanding can also be reduced via a reverse stock split.
- To do this, we need to calculate a weighted average of the company’s outstanding shares over the time period.
Public companies are required to report their number of shares outstanding in their quarterly and annual disclosures to the Securities & Exchange Commission. The earnings per share calculation for the year would then be calculated as earnings divided by the weighted average number of shares ($200,000/150,000), which is equal to $1.33 per share. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
In effect, it weights any change in the number of shares outstanding according to the length of time that change was in effect. Shares outstanding include shares owned by retail and institutional investors and restricted shares held by company officials and employees. Changes in the composition of the holdings do not change the number of total shares outstanding.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
New share issues, the exercise of stock options, conversion, and cancellations through buybacks will change the figure. Outstanding shares represent a company’s shares that are held by investors, whether they’re individual, institutional, or insiders. Investors can find the total number of outstanding shares a company has on its balance sheet.
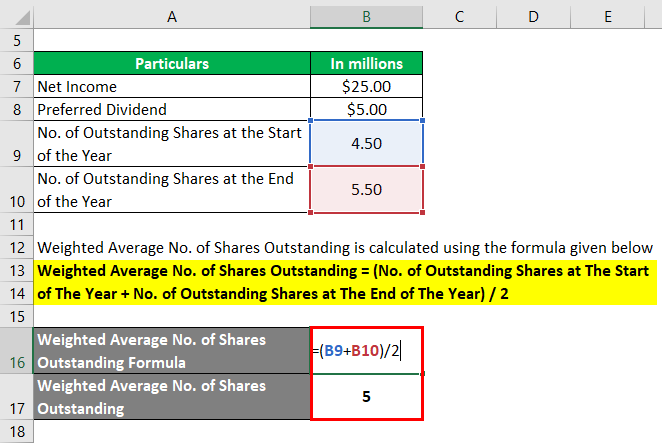
The key distinction between a simple average and a weighted average lies in the consideration of time. Among these, understanding the concept of Weighted Average Shares Outstanding (WASO) stands out due to its critical role in evaluating a company’s financial health and performance. Group 1 consists of 200,000 split shares that were effectively outstanding for the entire year.

